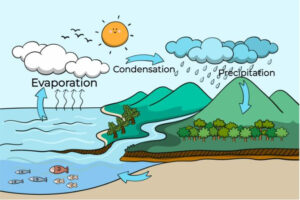
Evaporation
- Evaporation is the process that changes liquid water to gaseous water (water vapor).
- Water moves from the Earth’s surface to the atmosphere via evaporation.
- Evaporation occurs when energy (heat) forces the bonds that hold water molecules together to break.
Factors affecting evaporation
1. Temperature:
- On increasing the temperature the rate of evaporation also increases.
- At higher temperatures, the molecules are moving faster; therefore, it is more likely for a molecule to have enough energy to break away from the liquid to become a gas.
2. Wind speed:
- Wind speed and rate of evaporation are directly proportional to each other.
- As the wind speed increases, the rate of evaporation also increases.
3. Surface area:
- As the surface area increases, the rate of evaporation also increases.
- The more area is exposed to air, allowing water molecules to acquire more heat energy from the surroundings.
4. Humidity:
- Humidity and rate of evaporation are in inverse relation to each other.
- As the humidity decreases, the rate of evaporation increases.