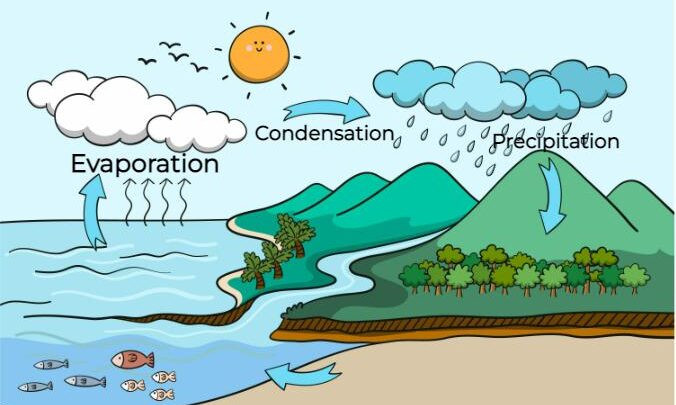
Here we given detail definition of evaporation. Here you will also study about Factors affecting evaporation. We have included many factors that affect the evaporation, like, temperature, wind speed, surface area and humidity. All Factors affecting evaporation are explain here briefly.
Evaporation
- Evaporation is the process that changes liquid water to gaseous water (water vapor).
- Water moves from the Earth’s surface to the atmosphere via evaporation.
- Evaporation occurs when energy (heat) forces the bonds that hold water molecules together to break.
Factors affecting evaporation
Temperature :
- On increasing the temperature the rate of evaporation also increases.
- At higher temperatures, the molecules are moving faster; therefore, it is more likely for a molecule to have enough energy to break away from the liquid to become a gas.
Wind speed :
- Wind speed and rate of evaporation are directly proportional to each other.
- As the wind speed increases, the rate of evaporation also increases.
Surface area :
- As the surface area increases, the rate of evaporation also increases.
- The more area is exposed to air, allowing water molecules to acquire more heat energy from the surroundings.
Humidity :
- Humidity and rate of evaporation are in inverse relation to each other.
- As the humidity decreases, the rate of evaporation increases.
Conclusion
- Here we have given detail about evaporation definition and Factors affecting evaporation.
- We have included all Factors affecting evaporation and discuss it briefly.
- This Factors affecting evaporation are very important while studying evaporation.
- Hope you like it.
Also Visit :
